Learning Outcomes
i. Comprehend the concept of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and their role in operating systems
ii. Identify and understand the function of basic icons and navigation elements in a GUI
iii. Demonstrate proficiency in navigating the desktop and file system using common mouse and keyboard shortcuts
iv. Customize the desktop environment to enhance user experience and personalize the workspace
Introduction
The graphical user interface (GUI) serves as the bridge between users and the complex world of computers, transforming the once intimidating command-line interface into an intuitive and visually appealing environment. This lesson introduces the fundamentals of GUIs, exploring their components, navigation techniques, and desktop customization options, empowering users to navigate the operating system with ease and efficiency.
i. Concept and Components of Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs)
A GUI is a software application that enables users to interact with a computer through visual elements such as icons, menus, and windows, rather than relying on text-based commands. GUIs have revolutionized computing, making computers more accessible and user-friendly.
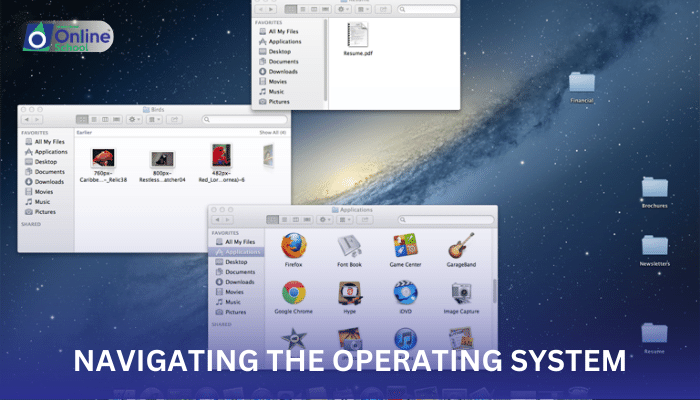
ii. Basic Icons and Navigation Elements in a GUI
Common icons found in a GUI include:
Desktop icons: Represent applications, documents, or folders stored on the computer.
Start menu or taskbar: Provides access to installed programs, system settings, and frequently used applications.
Window controls: Buttons for minimizing, maximizing, closing, and moving windows.
Menu bars: Contain options for performing actions within a specific application.
Toolbars: Provide quick access to frequently used functions.
Scroll bars: Allow users to navigate through long lists of items or documents.
iii. Navigating the Desktop and File System
The desktop is the primary workspace of a GUI, displaying icons representing files, folders, and applications. To navigate the desktop and file system effectively, users can employ various mouse and keyboard shortcuts:
Double-click: Launches an application, opens a folder, or executes a document.
Single-click: Selects an item or brings it into focus.
Right-click: Opens a context menu with options specific to the selected item.
Drag and drop: Moves or copies items by clicking and holding the mouse button while dragging the item to a new location.
Keyboard shortcuts: Provide quick access to common actions, such as saving files, copying text, and navigating between windows.
iv. Customizing the Desktop Environment
Users can personalize their desktop environment to enhance their experience and tailor it to their preferences. Common customization options include:
Changing the wallpaper: Replaces the default background image with a personal photo or pattern.
Arranging icons: Organizes icons in a preferred layout for easy navigation.
Adding widgets: Displays small applications or information panels on the desktop, providing quick access to weather, news, or other updates.
Adjusting color schemes: Changes the overall color palette of the desktop and application interfaces.
Graphical user interfaces have transformed the way we interact with computers, making them more accessible and user-friendly. By understanding the components, navigation techniques, and customization options of GUIs, users can navigate the operating system with ease, personalize their workspace, and enhance their overall computing experience.